HTML
CSS
HTML element
CSS class
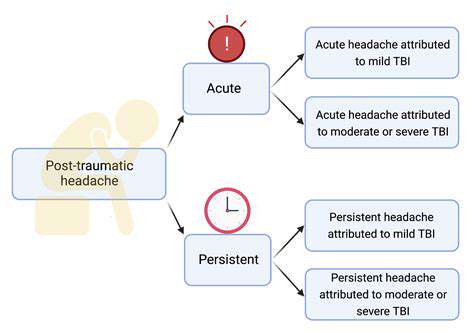
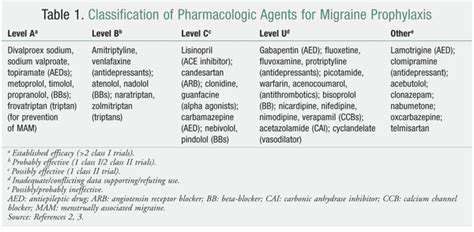
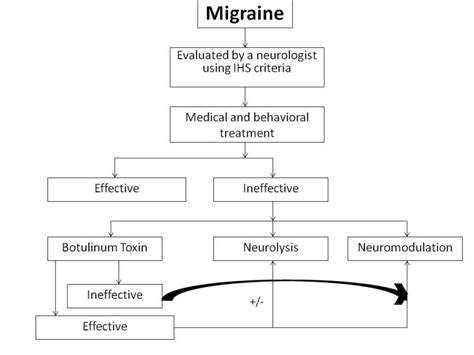
Migraine
MSG
味精(谷氨酸钠)作为潜在的偏头痛诱因

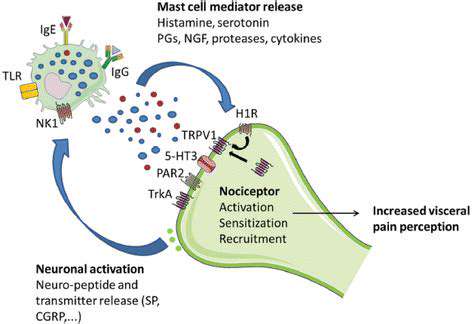
可能的MSG诱发偏头痛机制
潜在的细胞机制
谷氨酸钠(MSG),作为加工食品中广泛使用的增味剂,已引发
味精作为偏头痛诱因的研究和证据
早期研究和轶事证据
最初对味精与偏头痛之间联系的研究主要依赖于受试者自我报告的案例,许多受试者描述了类似的症状
Read more about 味精(谷氨酸钠)作为潜在的偏头痛诱因
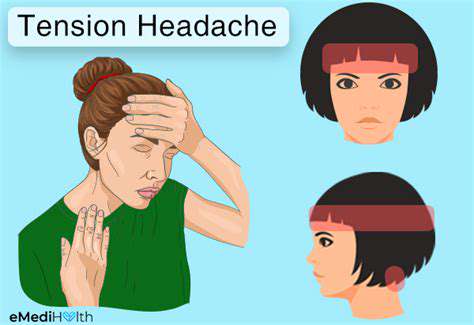
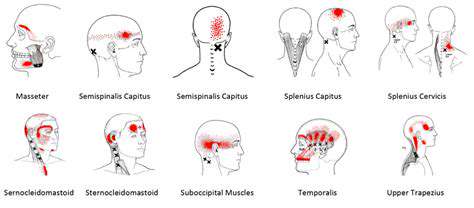
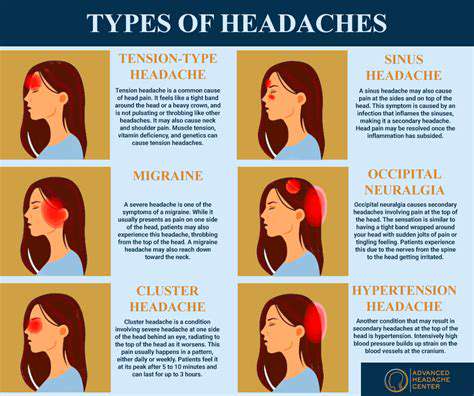
理解和管理常见的头痛。发现有效的策略来管理常见的头痛类型,包括紧张性头痛、鼻窦炎、偏头痛和眼睛疲劳。紧张性头痛是最常见的类型,通常源于压力和肌肉紧张,表现为额头周围的钝痛和紧绷感。了解如何识别症状,认识病因,并探索各种治疗选项来缓解不适。鼻窦炎以面部疼痛和压力为特征,可能由感染和过敏引起。理解及时诊断和量身定制的治疗计划以防止并发症的重要性。此外,深入探讨偏头痛发作——以强烈的搏动性疼痛和呕吐等附加症状为特征——并探索控制发作频率和严重性的急性和预防性治疗。眼睛疲劳可能伴随头痛,特别是在长时间使用屏幕后。通过20-20-20法则、屏幕调整和适当的照明等实用技巧来寻找缓解方案。无论你面临的是紧张性头痛还是其他与头痛相关的病症,这本全面的指南提供了关于症状识别、生活方式调整和何时寻求医疗建议的宝贵见解。---*有效管理你的头痛,重新获得生活质量!*
Jan 07, 2025