Health
Stress Management
HTML
CSS
Sleep Hygiene
共存する疾患を伴う頭痛の管理(例:線維筋痛症、IBS)
頭痛と慢性の病気の複雑な相互作用

Read more about 共存する疾患を伴う頭痛の管理(例:線維筋痛症、IBS)
一般的な深刻な症状とその影響を理解すること。この情報記事は、一般的な深刻な症状を認識する重要性と、それが全体的な健康に与える潜在的な影響を探ります。胸の痛みから説明のつかない体重減少、そして不安やうつ病などのメンタルヘルスの懸念まで、これらの症状を理解することは適時な医療介入にとって重要です。この記事は、深刻な症状を緩和することができる専門的な医療評価と生活習慣の変更の重要性を強調します。また、特定の警告サインに対して即座に助けを求めることの緊急性を強調しています。読者が症状を認識し、医療提供者に相談する方法を教育することによって、このリソースは個人が健康と幸福を優先してより良い結果を得ることを目指しています。
Nov 07, 2024
ストレスとその健康への影響を理解する
私たちの網羅的なガイドでストレスの複雑性を探ります。急性、エピソディック、慢性の異なるストレスのタイプと、それらがメンタルと身体の健康にどのように影響するかについて学びます。ストレスへの生物学的反応、長期的ストレスの心理的影響、ライフスタイルの選択との関連を発見します。マインドフルネスの実践、運動、サポートのある社会的ネットワークの構築を含む、ストレス管理のための効果的な戦略を提供します。身体の生理学的反応と、管理されていないストレスの長期的な結果を理解します。ストレスの引き金を認識し、積極的な対処戦略を採用することで、全体的な健康を改善し、より健康でバランスの取れた生活を送ることができます。
Nov 10, 2024
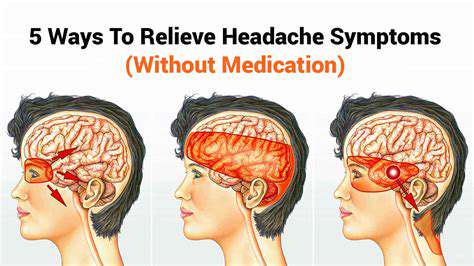
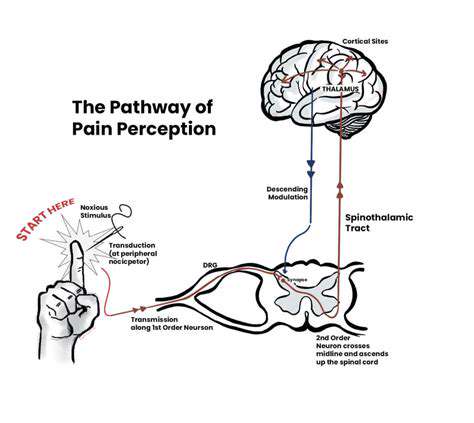
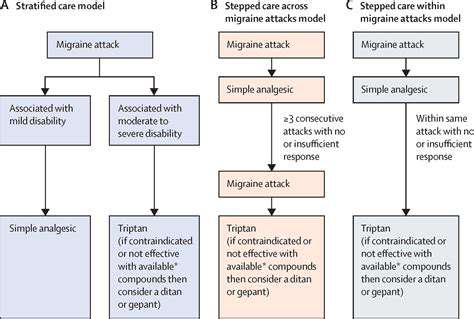
一般的な頭痛の種類とその治療を理解する緊張型頭痛から偏頭痛、群発性頭痛、副鼻腔炎による頭痛まで、様々な頭痛のタイプを探ります。これらの状態が時間と共にどのように進行し、症状を悪化させる可能性のあるさまざまな要因を学びます。このページでは、頭痛の痛みを和らげるためのストレス軽減技術やライフスタイルの変更を含む効果的な管理戦略についての洞察を提供します。また、専門的な助けを求めるべき時期や慢性頭痛患者のためのパーソナライズド治療オプションについても論じます。頭痛のトリガーと適切な介入を理解することで、健康を管理し、生活の質を向上させる方法を見つけましょう。
Nov 17, 2024
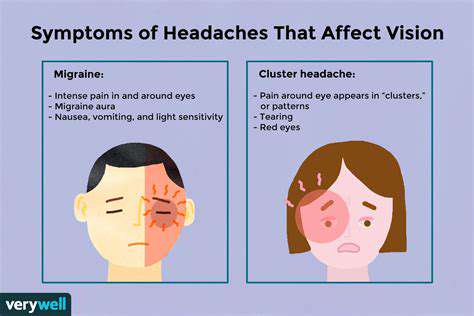
原因と緩和戦略 目の疲れ、偏頭痛、副鼻腔頭痛などの目と頭の痛みの一般的な原因を探ります。ストレスがこれらの状態にどのように影響するかを学び、注意すべき効果的な症状を発見します。目の痛みと頭痛の関連性を理解しましょう。緊張性頭痛や偏頭痛などがあります。このガイドでは、20-20-20ルールなどの自然療法から、処方薬や専門的な介入を含む医療処置まで、実行可能な緩和戦略を概説します。専門的な助けを求めるべき時期を認識することは、全体的な健康を維持するために重要です。目の健康と頭痛の間の複雑な関係を理解することで、あなたの幸福を向上させましょう。快適さとウェルビーイングを向上させるために、ぜひお読みください!
Jan 04, 2025
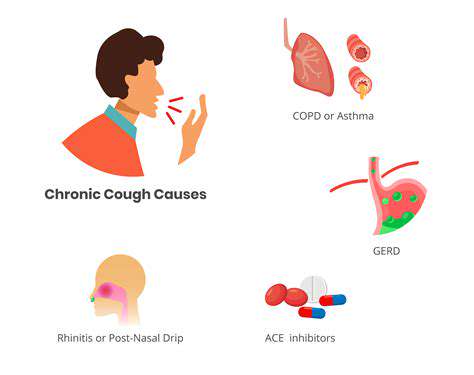
咳嗽によって引き起こされる頭痛の一般的な原因咳嗽によって引き起こされる頭痛の一般的な原因を探る包括的なガイドです。副鼻腔炎や偏頭痛から神経学的な問題まで、これらの状態が咳嗽発作中に不快感を引き起こす方法を学びましょう。めまいや鼻詰まりなど、注意が必要な伴う症状を発見し、いつ医療の助けを求めるべきかを学びましょう。また、咳によって引き起こされる頭痛を効果的に管理するための家庭療法、医療的介入、ライフスタイルの変更などの潜在的な治療法についても議論します。このしばしば見過ごされる症状に関する知識で自分を強化し、より良い健康に向けた積極的なステップを踏み出してください。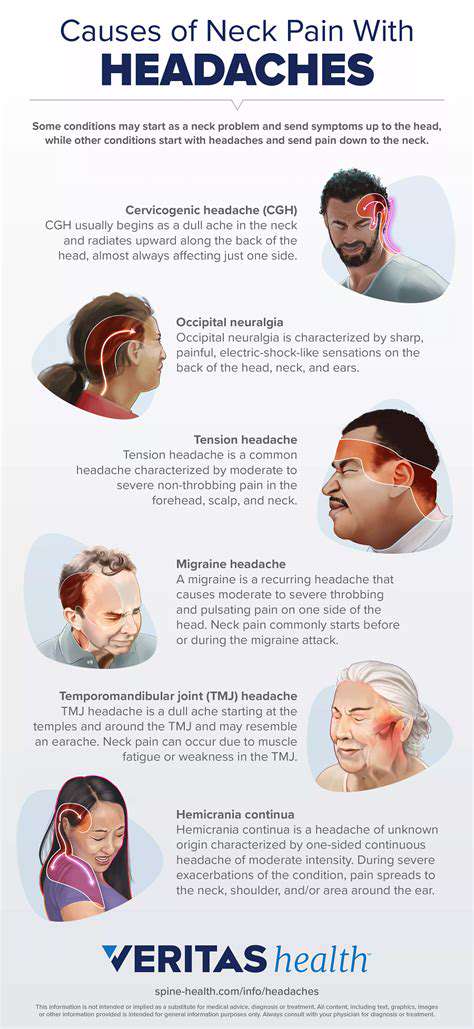
Mar 07, 2025