Health
Stress Management
HTML
CSS
Sleep Hygiene
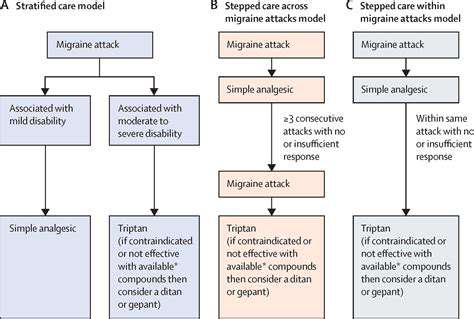
Quản lý đau đầu với các bệnh đồng tồn tại (ví dụ: viêm cơ xơ, hội chứng ruột kích thích)
Sự Tương tác Phức tạp giữa Đau Đầu và Các Bệnh Mãn tính

Hiểu về các Yếu tố Khởi phát
Đau đầu ảnh hưởng đến hàng triệu người trên toàn cầu, với các yếu tố khởi phát từ môi trường
Xác định các Yếu Tố Khởi Phát Đau Đầu trong Các Tình Trạng Đồng Vị
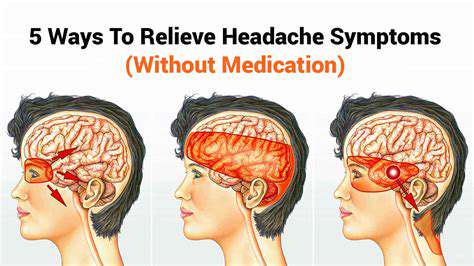
Xác định Đau Đầu do Căng Thẳng
Căng thẳng mãn tính kích hoạt trục dưới đồi-tuyến yên-tuyến thượng thận, tạo ra những thay đổi sinh lý dẫn đến đau đầu
Điều chỉnh lối sống để giảm đau đầu lâu dài

Ưu tiên giấc ngủ
Read more about Quản lý đau đầu với các bệnh đồng tồn tại (ví dụ: viêm cơ xơ, hội chứng ruột kích thích)
Tại sao chú ý đến các triệu chứng liên quan lại rất quan trọng cho sức khỏe tốt hơn
Oct 23, 2024
Hiểu về các triệu chứng nghiêm trọng phổ biến và ý nghĩa của chúng. Bài viết thông tin này khám phá tầm quan trọng của việc nhận biết các triệu chứng nghiêm trọng phổ biến và tác động tiềm tàng của chúng đối với sức khỏe tổng thể. Từ đau ngực đến giảm cân không rõ nguyên nhân và những lo ngại về sức khỏe tâm thần như lo âu và trầm cảm, việc hiểu những triệu chứng này rất quan trọng để can thiệp y tế kịp thời. Bài viết nhấn mạnh tầm quan trọng của các đánh giá y tế chuyên nghiệp và những thay đổi lối sống có thể làm giảm triệu chứng nghiêm trọng. Nó cũng làm nổi bật sự cấp bách của việc tìm kiếm sự giúp đỡ ngay lập tức cho các dấu hiệu cảnh báo cụ thể. Thông qua việc giáo dục độc giả về việc nhận biết triệu chứng và tham khảo các nhà cung cấp dịch vụ chăm sóc sức khỏe, tài nguyên này nhằm mục đích trao quyền cho các cá nhân để ưu tiên sức khỏe và phúc lợi của họ nhằm đạt được kết quả tốt hơn.
Nov 07, 2024
Hiểu về Căng Thẳng và Tác Động của Nó đến Sức Khỏe
Khám phá sự phức tạp của căng thẳng trong hướng dẫn toàn diện của chúng tôi. Tìm hiểu về các loại căng thẳng khác nhau - căng thẳng cấp tính, cục bộ và mãn tính - và cách chúng ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe tinh thần và thể chất. Khám phá các phản ứng sinh học với căng thẳng, những hệ lụy tâm lý của căng thẳng kéo dài và mối liên hệ với các lựa chọn lối sống. Chúng tôi cung cấp các chiến lược hiệu quả để quản lý căng thẳng, bao gồm thực hành chánh niệm, tập thể dục và xây dựng mạng lưới xã hội hỗ trợ. Hiểu các phản ứng sinh lý của cơ thể và các hậu quả lâu dài của căng thẳng không được kiểm soát. Bằng cách nhận ra các yếu tố kích hoạt căng thẳng của bạn và áp dụng các chiến lược đối phó chủ động, bạn có thể cải thiện sức khỏe tổng thể của mình và sống một cuộc sống khỏe mạnh, cân bằng hơn.
Nov 10, 2024
Hiểu Các Loại Đau Đầu Phổ Biến và Điều Trị của Chúng Khám phá các loại đau đầu - từ đau đầu do căng thẳng và đau nửa đầu đến đau đầu cluster và viêm xoang. Tìm hiểu cách những tình trạng này tiến triển theo thời gian và các yếu tố khác nhau có thể làm trầm trọng thêm các triệu chứng của bạn. Trang này cung cấp cái nhìn về các chiến lược quản lý hiệu quả, bao gồm các kỹ thuật giảm căng thẳng và thay đổi lối sống, để giảm đau đầu. Chúng tôi cũng thảo luận về thời điểm cần tìm kiếm sự giúp đỡ chuyên nghiệp và các lựa chọn điều trị cá nhân hóa cho những người bị đau đầu mãn tính. Khám phá cách kiểm soát sức khỏe của bạn và cải thiện chất lượng cuộc sống của bạn bằng cách hiểu những yếu tố kích thích và can thiệp phù hợp cho chứng đau đầu.
Nov 17, 2024
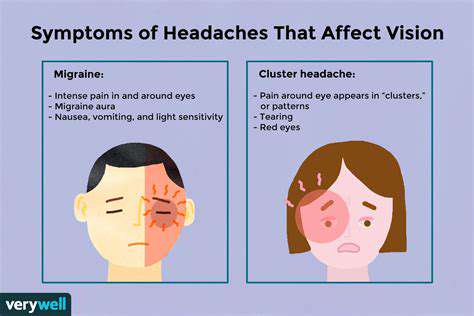
Nguyên nhân và Chiến lược Giảm đau Tìm hiểu về những nguyên nhân phổ biến gây ra cơn đau ở mắt và đầu, bao gồm mỏi mắt, đau nửa đầu, đau đầu do xoang và nhiều hơn nữa. Tìm hiểu cách căng thẳng ảnh hưởng đến những tình trạng này và phát hiện những triệu chứng hiệu quả để nhận biết. Hiểu mối liên hệ giữa đau mắt và đau đầu, như đau đầu do căng thẳng và đau nửa đầu. Hướng dẫn này phác thảo các chiến lược hành động để giảm đau, từ các biện pháp tự nhiên như quy tắc 20-20-20 đến các phương pháp điều trị y tế bao gồm thuốc theo toa và can thiệp chuyên nghiệp. Nhận biết khi nào cần tìm kiếm sự trợ giúp chuyên nghiệp rất quan trọng để duy trì sức khỏe tổng thể của bạn. Cải thiện sức khỏe của bạn bằng cách hiểu mối quan hệ phức tạp giữa sức khỏe mắt và đau đầu. Tiếp tục đọc để nâng cao sự thoải mái và sức khỏe của bạn ngay hôm nay!
Jan 04, 2025
Sự thay đổi tư thế có thể gây ra những thay đổi đáng kể đến sức khỏe và sự khỏe mạnh như thế nào
Feb 19, 2025
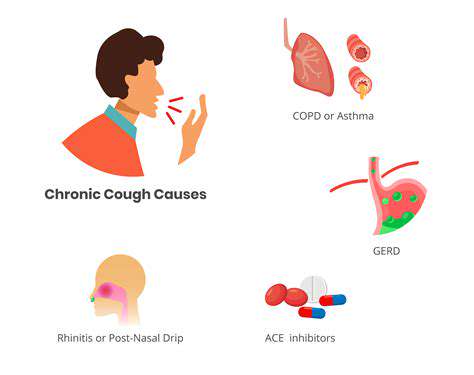
Các Nguyên Nhân Thường Gặp Gây Đau Đầu Khi Ho Khám phá những nguyên nhân phổ biến gây đau đầu khi ho trong hướng dẫn toàn diện của chúng tôi. Từ viêm xoang và chứng đau nửa đầu đến các vấn đề thần kinh, tìm hiểu cách những tình trạng này có thể dẫn đến sự khó chịu trong cơn ho. Khám phá các triệu chứng kèm theo cần chú ý, chẳng hạn như chóng mặt và ngạt mũi, và khi nào cần tìm sự trợ giúp y tế. Chúng tôi cũng thảo luận về các phương pháp điều trị tiềm năng, bao gồm các biện pháp tại nhà, can thiệp y tế và thay đổi lối sống, để quản lý hiệu quả cơn đau đầu do ho gây ra. Hãy tự trang bị kiến thức về triệu chứng thường bị bỏ qua này và thực hiện các bước chủ động hướng tới sức khỏe tốt hơn.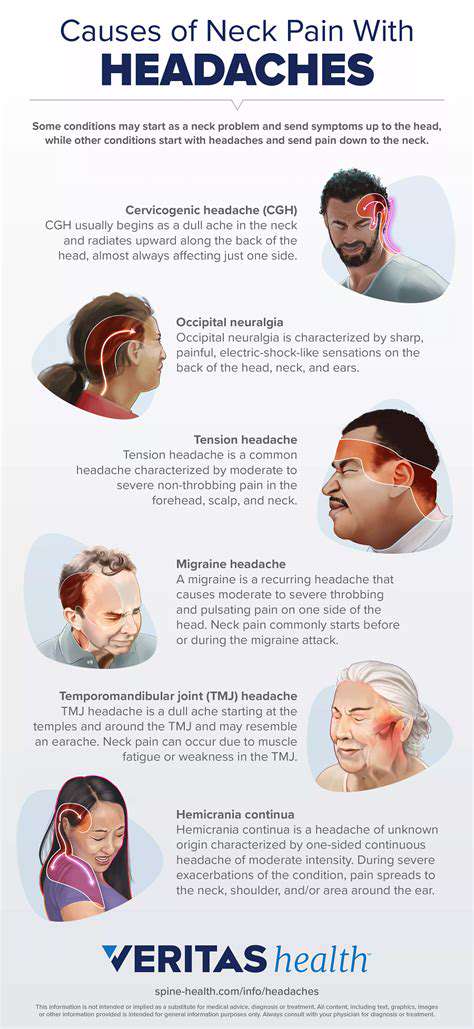
Mar 07, 2025
Đau đầu bên trái khi cúi xuống: Hiểu về các triệu chứng
May 01, 2025
Cân bằng công việc, cuộc sống và quản lý đau nửa đầu
May 25, 2025