Health
Stress Management
HTML
CSS
Sleep Hygiene
伴随疾病的头痛管理 (例如纤维肌痛、肠易激综合征)
头痛与慢性病的复杂相互作用

Read more about 伴随疾病的头痛管理 (例如纤维肌痛、肠易激综合征)
了解常见严重症状及其影响。本文探讨了识别常见严重症状及其对整体健康潜在影响的重要性。从胸痛到无法解释的体重减轻,以及焦虑和抑郁等心理健康问题,了解这些症状对及时医疗干预至关重要。文章强调了专业医疗评估和可以缓解严重症状的生活方式改变的重要性。它还突出了针对特定警告信号寻求即时帮助的紧迫性。通过教育读者识别症状和咨询医疗服务提供者,本文旨在使个人能够优先考虑他们的健康和福祉,以获得更好的结果。
Nov 07, 2024
理解压力及其对健康的影响
探索我们全面指南中压力的复杂性。了解压力的不同类型——急性、偶发性和慢性——以及它们如何影响心理和身体健康。发现压力的生物反应,长期压力的心理影响,以及与生活方式选择的联系。我们提供有效的压力管理策略,包括正念练习、锻炼和建立支持性的社交网络。了解身体的生理反应和未管理压力的长期后果。通过识别你的压力诱因并采取积极的应对策略,你可以改善整体健康并过上更健康、更平衡的生活。
Nov 10, 2024
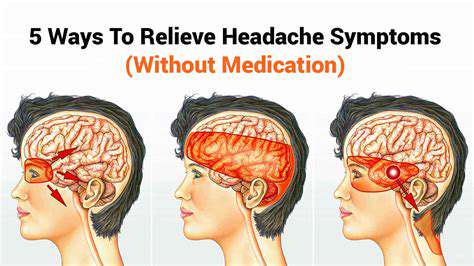
了解常见类型的头痛及其治疗探索头痛的类型——从紧张性头痛和偏头痛到丛集性头痛和鼻窦头痛。了解这些病症如何随时间推移而进展,以及可能加重症状的各种因素。此页面提供有效管理策略的见解,包括减压技巧和生活方式改变,以缓解头痛疼痛。我们还讨论了何时寻求专业帮助以及针对慢性头痛患者的个性化治疗选择。通过了解头痛的诱因和适当干预措施,发现如何掌控自己的健康,提高生活质量。
Nov 17, 2024
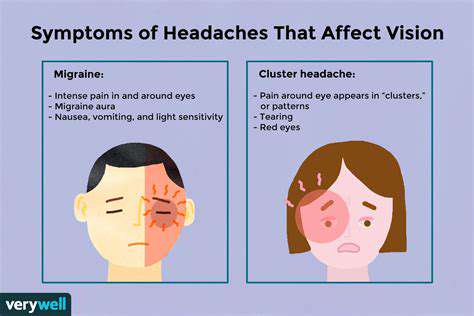
原因和缓解策略 了解眼部和头部疼痛的常见原因,包括眼疲劳、偏头痛、 sinus 头痛等。学习压力如何影响这些状况并发现有效的症状识别方法。理解眼痛与头痛之间的联系,比如紧张性头痛和偏头痛。本指南概述了可行的缓解策略,包括像20-20-20规则这样的自然疗法,以及处方药物和专业干预等医学治疗。识别何时寻求专业帮助对保持整体健康至关重要。通过了解眼健康与头痛之间的复杂关系来增强您的幸福感。继续阅读,提升您的舒适和健康!
Jan 04, 2025
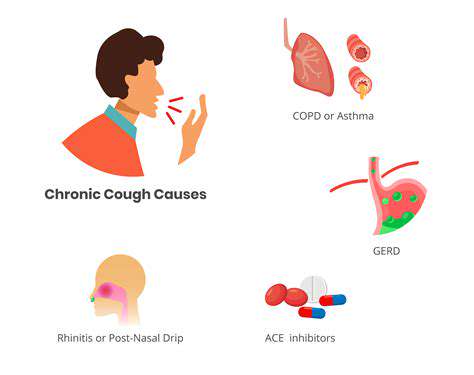
咳嗽引发头痛的常见原因探索咳嗽引发的头痛的常见原因,了解这些条件如何导致咳嗽时的疼痛。我们提供全面的指南。从鼻窦炎和偏头痛到神经系统问题,了解这些疾病如何在咳嗽发作时导致不适。发现伴随的症状,如头晕和鼻塞,以及何时寻求医疗帮助。我们还讨论可能的治疗方法,包括家庭疗法、医疗干预和生活方式的改变,以有效管理因咳嗽引起的头痛。通过了解这种常被忽视的症状,增强自己的健康意识,采取积极措施改善健康。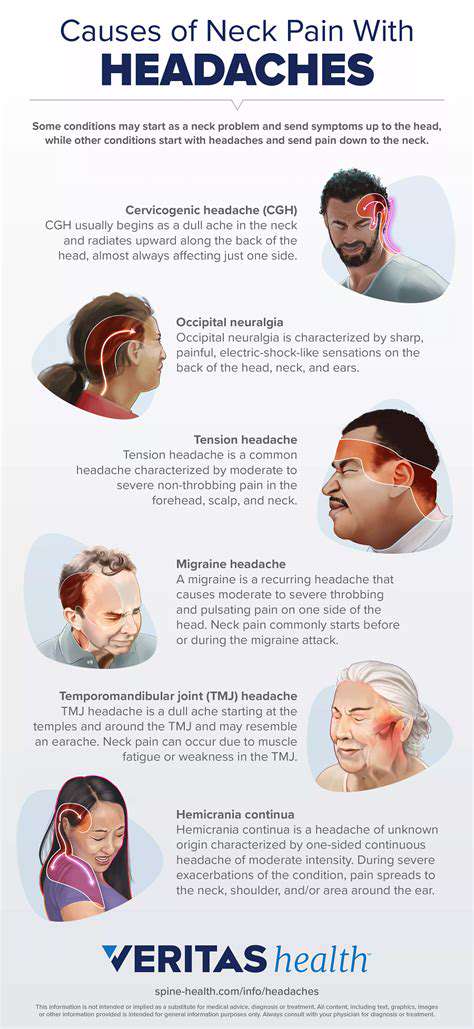
Mar 07, 2025