Health
Stress Management
HTML
CSS
Sleep Hygiene
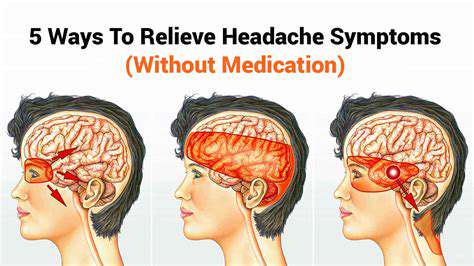
Zarządzanie bólem głowy przy współistniejących schorzeniach (np. fibromialgia, IBS)
Złożona interakcja między bólami głowy a przewlekłymi schorzeniami

Rozumienie czynników wyzwalających
Bóle głowy dotykają miliony ludzi na całym świecie, a czynniki wyzwalające obejmują wszystko od środowiska
Identyfikacja potencjalnych czynników wywołujących bóle głowy w współistniejących schorzeniach
Identyfikacja bólów głowy związanych ze stresem
Przewlekły stres aktywuje oś podwzgórze-przysadka-nadnercza, powodując zmiany fizjologiczne, które wywołują bóle głowy. M
Dostosowania stylu życia dla długotrwałego złagodzenia bólu głowy

Priorytet dla snu
Read more about Zarządzanie bólem głowy przy współistniejących schorzeniach (np. fibromialgia, IBS)
Dlaczego zwracanie uwagi na towarzyszące objawy jest kluczowe dla lepszego zdrowia
Oct 23, 2024
Zrozumienie powszechnych poważnych objawów i ich implikacji. Ten informacyjny artykuł bada znaczenie rozpoznawania powszechnych poważnych objawów i ich potencjalnych implikacji dla ogólnego zdrowia. Od bólu w klatce piersiowej po niewyjaśnioną utratę wagi oraz problemy zdrowia psychicznego, takie jak lęk i depresja, zrozumienie tych objawów jest kluczowe dla terminowej interwencji medycznej. Artykuł podkreśla znaczenie profesjonalnych ocen medycznych oraz zmian w stylu życia, które mogą złagodzić poważne objawy. Podkreśla również pilność poszukiwania natychmiastowej pomocy w przypadku konkretnych sygnałów ostrzegawczych. Edukując czytelników na temat rozpoznawania objawów i konsultacji z dostawcami usług medycznych, zasób ten ma na celu wzmocnienie jednostek w priorytetowym traktowaniu ich zdrowia i samopoczucia w celu uzyskania lepszych wyników.
Nov 07, 2024
Zrozumienie Stresu i jego Wpływu na Zdrowie
Zbadaj złożoność stresu w naszym kompleksowym przewodniku. Dowiedz się o różnych rodzajach stresu – ostrym, epizodycznym i przewlekłym – oraz o tym, jak wpływają one zarówno na zdrowie psychiczne, jak i fizyczne. Odkryj biologiczne reakcje na stres, psychologiczne konsekwencje długoterminowego stresu i powiązania ze stylem życia. Oferujemy skuteczne strategie zarządzania stresem, w tym praktyki uważności, ćwiczenia i budowę wspierających sieci społecznych. Zrozum reakcje fizjologiczne organizmu i długoterminowe konsekwencje nieradzenia sobie ze stresem. Rozpoznając swoje wyzwalacze stresu i przyjmując proaktywne strategie radzenia sobie, możesz poprawić swoje samopoczucie i prowadzić zdrowsze, bardziej zrównoważone życie.
Nov 10, 2024
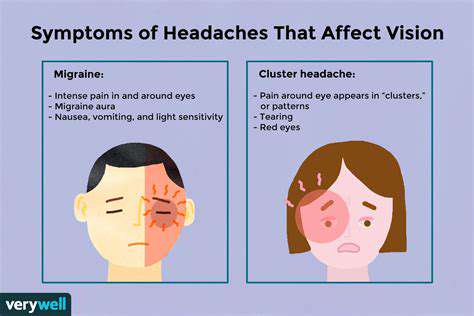
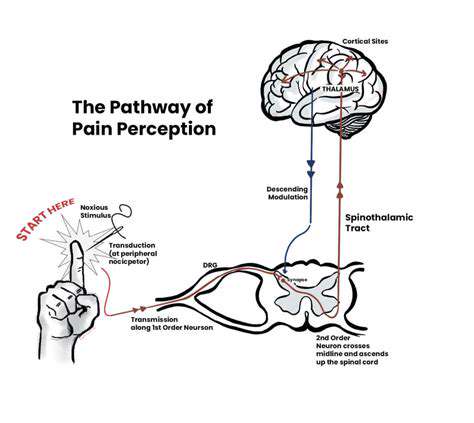
Zrozumienie Powszechnych Rodzajów Bólu Głowy i Ich Leczenia. Poznaj rodzaje bólów głowy - od napięciowych i migrenowych po klasterowe i zatokowe. Dowiedz się, jak te schorzenia rozwijają się z czasem oraz jakie różne czynniki mogą nasilać Twoje objawy. Ta strona oferuje spostrzeżenia dotyczące skutecznych strategii zarządzania, w tym technik redukcji stresu oraz zmian stylu życia, które mają na celu złagodzenie bólu głowy. Dyskutujemy również, kiedy warto szukać pomocy profesjonalnej oraz dostosowanych opcji leczenia dla osób cierpiących na chroniczne bóle głowy. Odkryj, jak przejąć kontrolę nad swoim zdrowiem i poprawić jakość życia, zrozumiejąc czynniki wyzwalające i odpowiednie interwencje w przypadku bólu głowy.
Nov 17, 2024
Przyczyny i strategie łagodzenia Odkryj powszechne przyczyny bólu oczu i głowy, w tym zmęczenie oczu, migreny, bóle głowy zatokowe i wiele innych. Dowiedz się, jak stres wpływa na te stany i poznaj skuteczne objawy, na które należy zwracać uwagę. Zrozum związek między bólem oczu a bólami głowy, takimi jak bóle głowy napięciowe i migreny. Ten przewodnik przedstawia wykonalne strategie ulgowe, od naturalnych środków, takich jak zasada 20-20-20, po leczenie medyczne, w tym leki na receptę i interwencje specjalistyczne. Rozpoznanie, kiedy należy szukać pomocy profesjonalnej, jest kluczowe dla utrzymania ogólnego zdrowia. Zwiększ swoje samopoczucie, rozumiejąc złożoną relację między zdrowiem oczu a bólami głowy. Czytaj dalej, aby poprawić swoje samopoczucie i komfort dzisiaj!
Jan 04, 2025
Jak zmiany w postawie mogą wywołać znaczące zmiany w zdrowiu i samopoczuciu
Feb 19, 2025
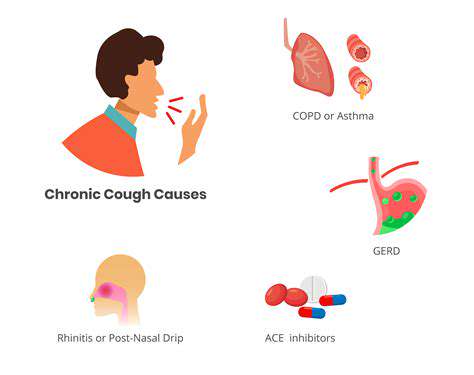
Częste przyczyny bólu głowy podczas kaszlu Zbadaj częste przyczyny bólu głowy wywołanego kaszlem w naszym kompleksowym przewodniku. Od zapalenia zatok i migren po problemy neurologiczne, poznaj, jak te schorzenia mogą prowadzić do dyskomfortu podczas ataków kaszlu. Odkryj towarzyszące objawy, na które należy zwrócić uwagę, takie jak zawroty głowy i zatory nosowe oraz kiedy szukać pomocy medycznej. Omawiamy również potencjalne metody leczenia, w tym domowe środki zaradcze, interwencje medyczne i zmiany stylu życia, aby skutecznie zarządzać bólem głowy wywołanym kaszlem. Wzmocnij swoją wiedzę na temat tego często pomijającego objawu i podejmij proaktywne kroki w kierunku lepszego zdrowia.
Mar 07, 2025
Ból głowy po lewej stronie głowy podczas schylania: zrozumienie objawów
May 01, 2025
Herbaty ziołowe, które mogą pomóc w łagodzeniu bólu głowy
May 08, 2025
Bilansowanie pracy, życia i zarządzania migreną
May 25, 2025
Bóle głowy z powodu odstawienia kofeiny: Jak sobie poradzić
Jun 03, 2025