Managing Headaches with Co existing Conditions (e.g., Fibromyalgia, IBS)
The Complex Interplay of Headaches and Chronic Conditions

Understanding the Triggers
Headaches affect millions worldwide, with triggers ranging from environmental factors to personal habits. Physical and emotional stress frequently leads to tension headaches, often described as a tight band around the head. Dietary influences like caffeine consumption patterns and specific food intolerances can also precipitate episodes. Many patients report weather changes, particularly shifts in barometric pressure, as consistent triggers.
Common dietary triggers include aged cheeses, processed meats, and alcohol - all containing vasoactive compounds. Sleep disturbances, whether insufficient sleep or irregular patterns, create physiological stress that may manifest as headache pain. Maintaining a trigger diary helps identify personal patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Classifying Headache Types
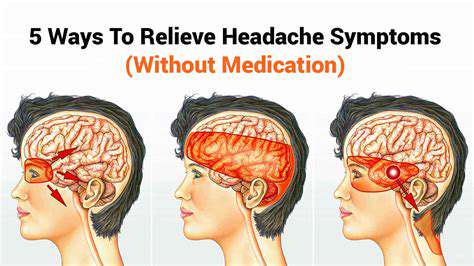
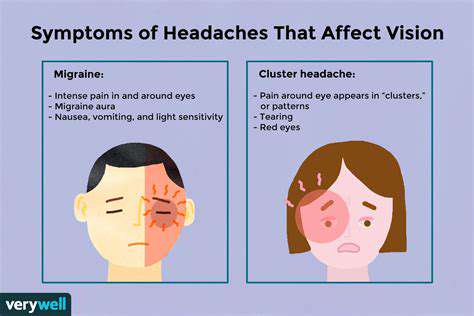
The headache spectrum includes several distinct clinical presentations requiring different management approaches. Migraine episodes typically involve unilateral pulsating pain with photophobia and nausea, sometimes preceded by aura symptoms. Tension-type headaches present as bilateral pressure without the systemic symptoms characteristic of migraines.
Cluster headaches represent a particularly severe variant with excruciating orbital pain lasting 15-180 minutes, often waking patients from sleep. Accurate classification guides therapeutic decisions, from abortive medications to preventive strategies, making proper diagnosis essential.
The Role of Genetics
Family studies demonstrate clear hereditary patterns in primary headache disorders. First-degree relatives of migraine sufferers have 2-4 times greater risk of developing similar symptoms, suggesting strong genetic components. Recent genome-wide association studies have identified multiple susceptibility loci, particularly for migraine with aura.
Diagnostic Approaches
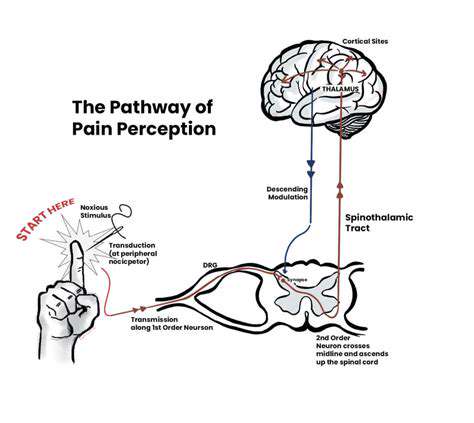
Comprehensive headache evaluation begins with detailed history-taking focusing on pain characteristics, associated symptoms, and temporal patterns. Neurological examination helps differentiate primary headaches from secondary causes. Red flag symptoms including thunderclap onset or progressive worsening warrant urgent neuroimaging to exclude serious pathology.
While most headaches represent primary disorders, clinicians must remain vigilant for secondary causes like intracranial lesions or vascular abnormalities. Specialty referral becomes necessary when standard therapies fail or when concerning features emerge during evaluation.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Effective headache management employs both pharmacological and non-pharmacological modalities. Behavioral interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy and biofeedback demonstrate particular efficacy for stress-related headaches. Dietary modification and sleep hygiene optimization serve as foundational preventive measures.
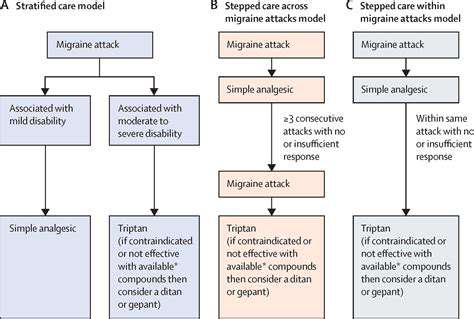
Acute therapies range from simple analgesics for mild episodes to triptans or gepants for moderate-severe migraines. Prophylactic medications including beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, or CGRP antagonists reduce attack frequency in chronic cases. Multidisciplinary approaches combining lifestyle modification, pharmacotherapy, and behavioral interventions yield optimal outcomes for refractory headaches.
Identifying Potential Headache Triggers in Co-existing Conditions
Identifying Stress-Related Headaches
Chronic stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, creating physiological changes that precipitate headaches. Muscular tension in cervical and cranial regions generates referred pain perceived as headache. Progressive muscle relaxation techniques and mindfulness meditation effectively interrupt this cycle.
Detailed headache logs should record stressors alongside pain characteristics to identify temporal relationships. Workplace ergonomic assessments often reveal modifiable factors contributing to musculoskeletal strain and subsequent headache development.
The Role of Diet and Hydration in Headache Development
Vasoactive substances like tyramine (in aged cheeses) and nitrites (in processed meats) trigger headaches through vascular and neural mechanisms. Dehydration reduces cerebral blood flow and electrolyte balance, activating trigeminal nociceptors. Maintaining consistent meal timing prevents hypoglycemia-related headaches.
Elimination diets help identify food triggers, though patients should maintain adequate nutrition during this process. Hydration monitoring using urine color charts provides objective measures of fluid status for headache-prone individuals.
The Connection Between Sleep Disorders and Headaches
Sleep architecture disturbances correlate strongly with headache frequency and severity. Obstructive sleep apnea causes intermittent hypoxia and hypercapnia, triggering morning headaches. Restless leg syndrome and insomnia similarly disrupt sleep continuity, lowering pain thresholds.
Polysomnography confirms sleep disorders when clinical suspicion exists. Continuous positive airway pressure therapy for apnea often dramatically improves comorbid headache disorders. Consistent bedtimes and wake times stabilize circadian rhythms, reducing headache occurrence.
The Impact of Hormonal Fluctuations on Headaches
Estrogen withdrawal preceding menses triggers migraines in susceptible women through effects on central pain pathways and cerebrovascular tone. Perimenopausal hormonal instability often exacerbates preexisting headache patterns. Oral contraceptives may improve or worsen symptoms depending on individual response.
Nonhormonal prevention strategies gain importance for women unable to tolerate hormonal therapies. Tracking headaches across menstrual cycles helps identify hormonally-sensitive patterns amenable to targeted treatment.
Migraine Triggers and Co-existing Conditions
Migraine comorbidity with mood disorders suggests shared pathophysiological mechanisms involving serotonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Weather changes may trigger attacks through barometric pressure effects on intracranial pressure. Photophobia and phonophobia reflect sensory processing abnormalities in migraine pathophysiology.
Comprehensive migraine management addresses psychiatric comorbidities alongside headache-specific therapies. Trigger avoidance combined with pharmacological and behavioral interventions provides optimal outcomes for complex cases.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-term Headache Relief

Prioritizing Sleep
Sleep quality significantly impacts headache disorders through multiple mechanisms. Maintaining consistent sleep-wake times synchronizes circadian rhythms, reducing headache susceptibility. Blue light exposure before bed delays melatonin onset, so limiting screen time in evenings improves sleep onset.
Sleep environment optimization includes temperature regulation (60-67°F ideal), noise control, and comfortable bedding. Chronic sleep restriction below 7 hours nightly increases inflammatory markers and headache risk substantially.
Nourishing Your Body
Anti-inflammatory diets emphasizing omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and magnesium demonstrate efficacy in headache prevention. Meal skipping triggers hypoglycemia and subsequent headaches, making regular balanced meals essential. Caffeine moderation prevents withdrawal headaches while avoiding excessive vasoconstriction.
Magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens and nuts may benefit migraineurs due to this mineral's role in neuronal excitability. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) supplementation shows promise for migraine prevention in clinical trials.
Managing Stress Effectively
Chronic stress promotes central sensitization, lowering pain thresholds and increasing headache frequency. Diaphragmatic breathing exercises activate parasympathetic responses, counteracting stress physiology. Regular aerobic exercise releases endorphins that modulate pain perception and reduce headache intensity.
Time management strategies prevent overwhelming stress accumulation. Cognitive restructuring techniques help reframe stress responses, reducing their headache-triggering potential. Consistent stress management practices create neurological changes that enhance resilience to headache triggers over time.
Staying Active and Engaged
Moderate aerobic exercise 3-5 times weekly reduces headache frequency through multiple mechanisms. Activity pacing prevents overexertion that could trigger exercise-induced headaches. Social engagement provides emotional support that buffers against stress-related headache exacerbations.
Regular physical activity upregulates endogenous pain-modulating systems, providing natural headache protection. Group exercise combines social and physical benefits, while mindfulness-based practices like tai chi offer dual stress reduction and gentle movement.